MATCGE: Difference between revisions
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
Our model is generic and include only one geographical region for now. It includdes intermediary deliveries, consumption (government and households), labour and investment. It can be used iteratively and a dynamically integrated version is under development. | Our model is generic and include only one geographical region for now. It includdes intermediary deliveries, consumption (government and households), labour and investment. It can be used iteratively and a dynamically integrated version is under development. | ||
The main specificity of our model is that material flows are endogenously adjusted. Underlying material flows are indexed <math>m \in M</math> and are linked to economic flows through material intensities <math>\theta_{m}</math>: <math>X_{mij}=\theta^X_{m}X_{ij}</math>, <math>C_{mih} | The main specificity of our model is that material flows are endogenously adjusted. Underlying material flows are indexed <math>m \in M</math> and are linked to economic flows through material intensities <math>\theta_{m}</math>: <math>X_{mij}=\theta^X_{m}X_{ij}</math>, <math>C_{mih}=\theta^C_{m}C_{ih}</math>. | ||
Material input is a natural resource in production: <math>R_{mi}=\rho_{mi}Y_i</math>. Waste comes from consumption, capital depreciation and a share <math>\epsilon</math> of material in production. | Material input is a natural resource in production: <math>R_{mi}=\rho_{mi}Y_i</math>. Waste comes from consumption, capital depreciation and a share <math>\epsilon</math> of material in production. | ||
Revision as of 11:27, 19 May 2023
General Scope and Connection with Climate Mitigation
Introduction
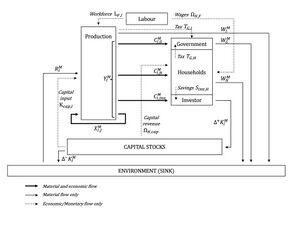
We introduce a CGE model that endogenously includes physical flows subject to material balance constraints. We propose a new framework that more accurately describes the interaction between transaction values and material flows, and thereby becomes particularly relevant for the ex ante analysis of CE policies and autonomous developments.
The model structure is very generic and has the following structure: firms producing goods , factors of production , and households and institutions . We have the following variables: for output by firms (which equals sales and total production costs), where we may omit the subscript for convenience as we do not use the symbol for other agents. for intermediates from firms to firms , using the symbol equivalently (alias) to . is factor use by firms, and is supply by consumers. is consumption by households, respectively. is taxes on resource use or waste generation.
Model Scope
Our model is generic and include only one geographical region for now. It includdes intermediary deliveries, consumption (government and households), labour and investment. It can be used iteratively and a dynamically integrated version is under development.
The main specificity of our model is that material flows are endogenously adjusted. Underlying material flows are indexed and are linked to economic flows through material intensities : , .
Material input is a natural resource in production: . Waste comes from consumption, capital depreciation and a share of material in production.
Note that it is possible to include as many materials as needed.
Model Development
- Status: the CGE model with endogenous material flows has a robust generic theoretical basis and the code to illustrate it. Further developments include: adding stock vintages, more precise Circular Economy elements, quality differentiation.
- Environment: python.
- Documentation: available for current version of the model.
- Source code: available for the static and iterative model. Time-integrated version is still under development.
Circular Economy Features
This section provide the CE features of the model
R Words coverage and implemented in the model
CE strategies and connection with climate change mitigation.
Synergies and trade-off between the R word in the context of the stylized model
Insights for Analytical Framework
This section should highlight the features relevant for the CIRCOMOD analytical framework. They should be linked with the previous section which provide more details.
- Key mechanisms and interactions within CE strategies that lead to changes in GHG emissions.
- Tool exploration (demonstrating ideas before implementing them in large-scale quantitative models)
- Communication key CE dynamics (to the broader audience)
Refinement, Integration, Future Development
The following sections are optional and should be completed only if they are relevant.
Refinement process
Please describe how the stylized model will be improved/refined in the CIRCOMOD project.
Integration
Highlight the features to be integrated in larger model in the CIRCOMOD project.
Future features of the model
Not yet implemented, planned model developments, if any.