CIRCEE
General Scope and Connection with Climate Mitigation
- Introduction
The decarbonization of our production processes and consumption of products and materials have a key role to play in achieving climate targets. One effective way to achieve this is by shifting from a linear economic system to a circular one, which emphasizes resource efficiency and reducing GreenHouse Gases emissions. The integration of circular economy poses many challenges to the IAM modeling community, including accounting for physical material flows, thermodynamics limits, and waste flows. CIRCEE (CIRCular Energy Economy), developed by the RFF-CMCC European Institute on Economics and the Environment, addresses these challenges by developing a stylized dynamic model. The stylized model will serve as a modeling starting point for the IAM community and will help mapping circular economy strategies into the existing climate scenarios.
- Model Scope.
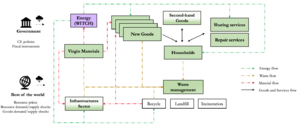
CIRCEE is a stylized dynamic general equilibrium model that monitors physical material and waste stock/flows. It incorporates key industrial ecology principles to evaluate how circular economy strategies and enablers can decrease future greenhouse gas emissions and enhance resource efficiency, especially in resource-poor economies. The main focus of CIRCEE is on countries that may become relatively less reliant on resources in the the long run due to the adoption of circular economy strategies and new business models, such as the sharing economy and digitalization.
The current geographical scope of CIRCEE is on Japan and South Korea. These countries are being studied first because they are among the least resource-rich economies in the OECD. Circular economy and new business models are essential for addressing climate change, improving resource security and promoting economic growth in these countries. While data availability will determine which additional OECD countries can be added to the model in the future, users may add other countries themselves, provided there is enough data to calibrate the model.
Users of CIRCEE can simulate the model for any desired number of years, using 2018 as the base year value, provided that the users have a clear trajectory or exogenous variables. The model has a yearly time step.
Intratemporal and Intertemporal decisions between different types of goods and services and different input mix, Disaggregation into nine sectors, Aggregate Primary (Virgin) Material and Aggregate Secondary (Recycled) Material, 10 products. On the energy side, CIRCEE is soft-linked to WITCH xxxxxxx
- Specify: Stock or Flow.
- Model documentation: in progress. Not yet available.
- Model development status
- Model source code (relative to milestone M24). The model uses the software platform Dynare (https://www.dynare.org). To run Dynare, you will need either Matlab, Julia or GNU Octave.
Circular Economy Features
- R Words coverage and implemented in the model
CIRCEE provides a broad perspective on the economic and natural resource demand implications of a circular economy by integrating many different circular economy strategies.
- CE strategies and connexion with climate change mitigation
- Synergies and trade-off between the R word in the context of the stylized model
Insights for Analytical Framework
- Key mechanisms and interactions within CE strategies that lead to changes in GHG emissions.
- Tool exploration (demonstrating ideas before implementing them in large-scale quantitative models)
- Communication key CE dynamics (to the broader audience)
Refinement and Integration
- Explain the iterative process of refining the stylized models by incorporating results emerging from other models
- Discuss how the stylized models can be integrated into larger modeling efforts to assess the potential of CE in climate change mitigation more comprehensively.