STYLIE
General Scope and Connection with Climate Mitigation
Introduction
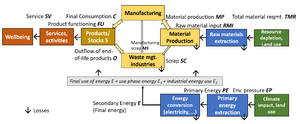
STYLIE (from Stylistic industial ecology (IE) model) is a simple accounting tool to capture the major service flows, product stocks, and energy and material flows in a circular economy. It has a comprehensive scope, as it links service provision (a major constituent of human wellbeing) with envionmental pressures (such as resource extraction and climate impact). It's system definition, which is based on the concept of the energy service cascade is shown below.
Model Scope
STYLIE can be applied at any geographical, service sector, and material scale. As an accounting model, it does not generate new results, but uses results from existing scenarios to develop a set of indicators and show where in the energy service cascade the decoupling happens.
The accounting equations of STYLIE (see figure on the right) follow the scheme of the famous IPAT accounting equation (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/I_%3D_PAT), as they expand the total pressure indicator into the different system variables, rearranging them to a decoupling factor for each stage in the energy service cascade.
Model Development
- Status: Under implementation
- Environment: javascript
- Documentation: https://github.com/Nilly92/IEF_Visualization/ (will be made publicly available once the implementation is mature)
- Source code: https://github.com/Nilly92/IEF_Visualization/ (will be made publicly available once the implementation is mature)
- Main references:
- For the stock-flow-service nexus in the energy service cascade (system definition), see Bergsdal et al. (2007), DOI 10.1080/09613210701287588 // Kalt et al. (2019), DOI 10.1016/j.erss.2019.02.026 // ; Haberl et al. (2017), DOI 10.3390/su9071049
- For existing examples of the accounting equation, see the description of the IPAT equation (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/I_%3D_PAT) as well as the IE literature: Carmona et al. (2022), DOI 10.1016/j.egyr.2022.10.086 // Tanikawa et al. (2021), DOI 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125450
Circular Economy Features
This section provide the CE features of the model
R Words coverage and implemented in the model
CE strategies and connection with climate change mitigation.
Synergies and trade-off between the R word in the context of the stylized model
Insights for Analytical Framework
This section should highlight the features relevant for the CIRCOMOD analytical framework. They should be linked with the previous section which provide more details.
- Key mechanisms and interactions within CE strategies that lead to changes in GHG emissions.
- Tool exploration (demonstrating ideas before implementing them in large-scale quantitative models)
- Communication key CE dynamics (to the broader audience)
Refinement, Integration, Future Development
The following sections are optional and should be completed only if they are relevant.
Refinement process
Since not all models will be able to calculate all variables in the system definition of STYLIE, the accounting equations (see above) will be simplified (aggregated) or modified so that the system definition and salient stocks and flows of the different models can be depicted.
Integration
Building on model results supplied to the CIRCOMOD data hub, STYLIE-based visualisations will be implemented on the project's homepage.
Future features of the model
Different visualisations and new indicators will be developed to address the different research questions.